Introduction to Data Management
Data management is a control program functions that provide access to data sets, enforce data storage conventions, and regulate the use of input or output devices. In all information systems, data resources must be organized and structured in some logical manner so that they can be accessed easily, processed efficiently, retrieved quickly, and managed effectively. This blog entry will first introduce about the fundamental data concepts of data management, then we will look at the changes of data management technology : from traditional file to data warehouse.
Fundamental Data Concepts
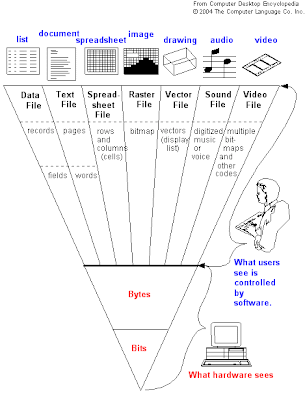
These fundamental concepts are all about how data are organized in information systems. If there is no systematic way to store and retrieve data, it is too difficult to get any information from an information system. Therefore, data resource should be organized in some logical manner. Data are logically organized into characters, fields, records, files, and database.
Character: A character is the most elementary logical data element, whereas bit and byte are basic physical storage elements. A character consists of a single alphabetic letter, numeric digit, or special symbol. The character is equivalent to a byte.
Field: The next higher level of data is the field. A field consists of a grouping of related characters. For example, a set of characters in a customer's name makes a name field. A field represents an attribute of an entity.
Record: A record is a collection of related fields. The record represents a collection of attributes that describe an entity.
File: A set of related records makes a file. For example, a customer file consists of many records of customers.
Database: A database is an integrated collection of logically related files. A database combines several records previously stored in separated files.
The Evolution of Data Management Technology
Traditional File Processing
It refers to collections of applications that each define and manage their own files. In the traditional file approach that was used in business data processing for many years, each business application was designed to use one or more specialized data files containing only specific types of data records. Meanwhile each department in the organization will have the same data which are organized, stored, and processed in independent files of data records.An example for traditional file processing is the students data in university : student's address may be needed for registering, library management, financial office, grade reporting and other purpose. Each applications separatelt maintains its data files and programs to manipulate those files. Therefore big posible to comes out different formats for the same data(e.g. length of names), and may cause redundant of updates(e.g. change of address). So what are the drawbacks of traditional file processing?
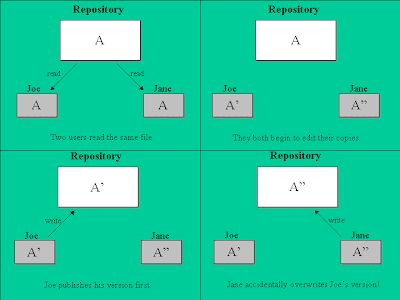
Problems With Traditional File Processing
Due to traditional file processing turned up to be too cumbersome, costly, and inflexible to supply the information needed for modern business to manage their information systems, it gradually replacing by the database management approach, which we will discuss afterward. Overall file processing systems had the following major problems :
(i)Data Redundancy
Means that separate files created problems of redundancy in defining and storing data. Each independent data files included a lot of duplicated data, which is the same data were recorded and stored in several files. This not only caused wasted of storage space, as well as redundant efforts to enter replicated data and maintain its consistency.
(ii) Lack of Data Integration
Since having data in independent files, it makes more harder for it to provide end users with information for ad hoc requests that required accessing stored in several different files. Special computer programs had to be written to retrieve data from each independent file. This retrieval was so difficult, time-consuming, and costly for some organizations taht it was impossible to provide end users or management with such information.
(iii) Data Dependence
There will be a problem of data definition in application program, where the program valid for only one database with a fixed structure. The organization of files, their physical locations and storage hardware, and the application software used to access those files is depended on one another.
(iv) Lack of Data Integrity or Standardization
Traditional file processing give tendency to separate and isolate logically-related data. Those subsequent data models requires more capture on information because these data elements is to be defined differently by different end users and applications, and appears to be no standardization.
For example :
End User 1 : Address
End User 2 : Addresses
End User 3 : Add
Database Management Approach
Database Management Approach has been created to encounter the main four problems with traditional file processing. It consolidates data into databases that can be accessed by different programs through the usage of database management systems(DBMS).
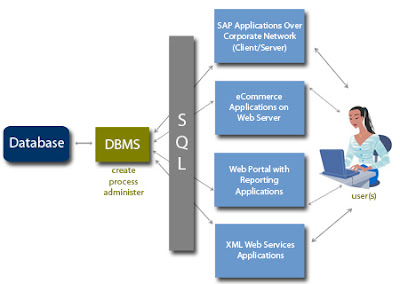
Database Management System (DBMS)
Database Management System (DBMS) is the main software tool of the database management approach, because it controls the creation, maintenance and use of the databases of an organization and its end users.
DBMS process and organize huge amounts of data and are a vital part of computer systems.
For example, a marketing manager can access a vast store of data on existing and potential customers from surveys, their Web habits, and their past purchases. This information can help the manager sell products and services.
A corporate lawyer has access to past cases and legal opinions from sophisticated legal databases. This information can help the lawyer win cases and protect the organization legally. Regardless of your students’ majors in school, using database management systems will likely be a critical part of their job.
Other examples for DBMS:
•Microcomputer DBMS package
E.g. :MS Access 2003
•Mainframe and server versions
E.g. :Oracle Database 10g, IBM DB2 UBD 8.2, Microsoft SQL Server 2005, Sybase ASE 15
•Open Source DBMS
E.g. :MySQL 5.0
The three major functions of a DBMS are:
1.To create new databases and database applications
2.To maintain the quality of the data in an organization’s databases
3.To use the databases of an organization to provide the information needed by its end users
Database Development involves defining and organizing the content, relationships and structure of the data needed to build a database.
Database Application Development involves using a DBMS to develop prototypes of queries, forms, reports and Web pages for a proposed business application.
Database Maintenance involves using transaction processing systems and other tools to add, delete, update and correct the data in a database.
The primary use of a database by end users involves employing the Database Interrogation capabilities of a DBMS to access the data in a database to selectively retrieve and display information and produce reports, forms and other documents.
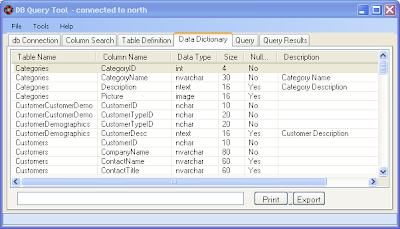
Data Dictionary is a software module and database containing descriptions and definitions, that is, metadata, concerning the structure, data elements, interrelationships and other characteristics of a database.
Types of Databases
The 4 types of databases used by business organizations are:
1.Operational Databases
- Also called subject area databases (SADB), transaction database and production database
- Store detailed data needed to support the business processes and operation of a company
- E.g., customer databases, human resource databases, inventory databases
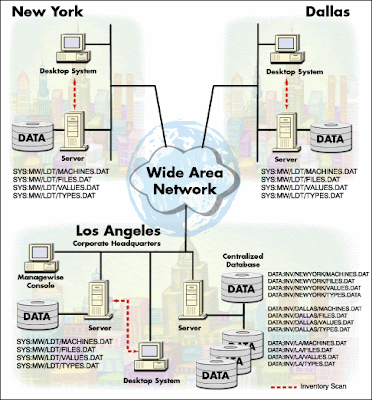
2.Distributed Databases
- The portions of a database at remote sites where the data are most frequently referenced
- Sharing of data is made possible through a network that interconnects the distributed databases
- Any change of data can be accomplished in one of two ways, which is replication or duplication
3.External Databases
- Databases available for a fee from commercial online services, or free from the Web
- E.g., hypermedia databases, statistical databases, bibliographic and full text databases
- Or search engines like, Google or Yahoo
4.Hypermedia Databases
- Documents containing multiple forms of media that can be interactively searched like Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)
- E.g., text, graphics, video and sounds
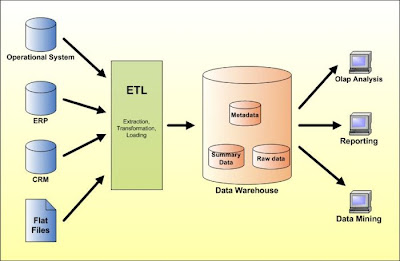
Data Warehouse
Data Warehouse is an integrated collection of data extracted from operational, historical and external databases that have been cleaned, transformed and cataloged for retrieval and analysis (data mining) to provide business intelligence for business decision making.
Data warehouses may be divided into data marts which are the subsets of data that focus on specific aspects of a company (department or business process).
Data Mining
Data Mining is where using special purpose software to analyze data from a data warehouse to find hidden patterns and trends.
For example, many companies use data mining to:
- Perform “market-basket analysis” to identify new
product bundles
- Find root cause of qualify or manufacturing problems
- Prevent customer attrition and acquire new customers
- Cross-sell to existing customers
- Profile customers with more accuracy
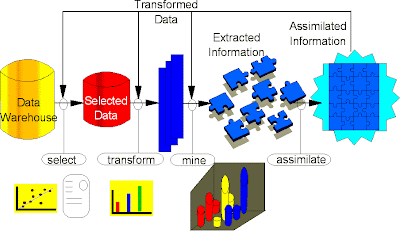
But, its main purpose is to provide decision support to managers and business professionals through knowledge discovery.
It also analyzes vast store of historical business data and tries to discover patterns, trends, and correlations hidden in the data that can help a company improve its business performance.
In this globalizations era, data are a vital organizational resource that needs to be managed like other important business assets. Today’s business enterprises cannot survive or succeed without quality data about their internal operations and external environment.
That’s why organizations and their managers need to practice data resource management, a managerial activity that applies information systems technologies like database management, data warehousing and other data management tools to the task of managing an organization’s data resources to meet the information needs of their business stakeholders.